Java Program to input a number using Scanner class and display its value
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Number you entered is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two numbers using Scanner class and add them
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,sum;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Second Number ");
b=sc.nextInt();
sum=a+b;
System.out.println("Sum of numbers is " + sum);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two numbers and find their difference
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,diff;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Second Number ");
b=sc.nextInt();
diff=a-b;
System.out.println("Difference of two numbers is " + diff);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two numbers and find their product
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,product;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Second Number ");
b=sc.nextInt();
product=a*b;
System.out.println("Product of two numbers is " + product);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two numbers and find their quotient
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,quotient;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Second Number ");
b=sc.nextInt();
quotient=a/b;
System.out.println("Quotient of two numbers is " + quotient);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two numbers and find their remainder
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,remainder;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First number");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Second Number ");
b=sc.nextInt();
remainder=a%b;
System.out.println("Remainder of two numbers is " + remainder);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input side of square and find area of square
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int side,area;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Side of square ");
side=sc.nextInt();
area=side*side;
System.out.println("Area of Square is " + area);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input side of square and find perimeter of square
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int side,perimeter;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Side of square ");
side=sc.nextInt();
perimeter=4*side;
System.out.println("Perimeter of Square is " + perimeter);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find area of rectangle
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int length,breadth,area;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Length of rectangle");
length=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Breadth of rectangle");
breadth=sc.nextInt();
area=length*breadth;
System.out.println("Area of Rectangle is " + area);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find perimeter of rectangle
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int length,breadth,perimeter;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Length of rectangle");
length=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Breadth of rectangle");
breadth=sc.nextInt();
perimeter=2*(length+breadth);
System.out.println("Perimeter of Rectangle is " + perimeter);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find volume of box
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int width,depth,height,volume;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Width of Box");
width=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Depth of Box ");
depth=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter Height of Box");
height=sc.nextInt();
volume=width*depth*height;
System.out.println("Volume of Box is " + volume);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input a decimal point value and display it using Scanner Class
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
float a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a decimal point Number ");
a=sc.nextFloat();
System.out.println("Decimal Point Number is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input a String and display value
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("String you entered is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to enter a double value and display it
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Decimal point number");
a=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Decimal Point Number of Double datatype number is "+a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to input two Strings and concatenate them
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b,c;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter First String ");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter Second String ");
b=sc.next();
c=a+b;
System.out.println("Concatenated String is " + c);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to enter a boolean variable and display its value
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
boolean a;
a=true;
System.out.println("Value of boolean variable is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find area of circle and it also includes PI Constant of Math Class
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double radius,area;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter radius of circle");
radius=sc.nextDouble();
area=Math.PI*radius*radius;
System.out.println("Area of Circle is " + area);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to circumference of circle it also includes PI Constant of Math Class
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double radius,circumference;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter radius of circle");
radius=sc.nextDouble();
circumference=2*Math.PI*radius;
System.out.println("Circumference of Circle is " + circumference);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate if statement
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“Enter a number “);
a=sc.nextInt();
if(a==10)
{
System.out.println(“Number you entered is 10”);
}
else
{
System.out.println(“Number you entered is not equal to 10”);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate switch statement
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int day;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Day from 1 to 7");
day=sc.nextInt();
switch(day)
{
case 1:
System.out.println("monday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("tuesday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("wednesday");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("thursday");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("friday");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("saturday");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("sunday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("enter a day between 1 and 7");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to make a menu driven program
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static float findarea(Scanner sc)
{
float area,radius;
System.out.println("Enter Radius of Circle");
radius=sc.nextFloat();
area=radius*radius*3.14f;
return area;
}
public static float findcircumference(Scanner sc)
{
float circumference,radius;
System.out.println("Enter Radius of Circle");
radius=sc.nextFloat();
circumference=radius*radius*3.14f;
return circumference;
}
public static int findareasquare(Scanner sc)
{
int side,area;
System.out.println("Enter Side of Square");
side=sc.nextInt();
area=side*side;
return area;
}
public static int findperimetersquare(Scanner sc)
{
int side,p;
System.out.println("Enter Side of Square");
side=sc.nextInt();
p=4*side;
return p;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int choice;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int temp;
float temp1;
while(true)
{
System.out.println("1. Area of circle ");
System.out.println("2. Circumference of circle");
System.out.println("3. Area of Square");
System.out.println("4. Perimeter of Square");
System.out.println("5. Exit");
System.out.println("Enter a Choice from 1 to 5 ");
choice=sc.nextInt();
if(choice==1)
{
temp1=findarea(sc);
System.out.println("Area is " + temp1);
}
if(choice==2)
{
temp1=findcircumference(sc);
System.out.println("Circumference is " + temp1);
}
if(choice==3)
{
temp=findareasquare(sc);
System.out.println("Area of Square is "+temp);
}
if(choice==4)
{
temp=findperimetersquare(sc);
System.out.println("Perimeter is "+ temp);
}
if(choice==5)
{
break;
}
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to calculate Simple Interest based on principal amount, rate of interest and time in years
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
double p,r,t,si;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Principal Amount ");
p=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter Rate of Interest ");
r=sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("Enter Time in Years ");
t=sc.nextDouble();
si=(p*r*t)/100;
System.out.println("Simple Interest is " + si);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate final keyword
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
final String name="Raman";
System.out.println("Value in final variable name is " + name);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check whether boiling point of water is 100 or not
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int temp;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Temperature of Water ");
temp=sc.nextInt();
if(temp==100)
{
System.out.println("Temperature is equal to Boiling Point of Water ");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Temperature is not equal to Boiling Point of Water ");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check for eligibility to vote
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int age;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Age of Candidate ");
age=sc.nextInt();
if(age>=18)
{
System.out.println("Eligible to Vote");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Not Eligible to Vote");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find grade of student
if marks are between 80 and 100 grade is A
if marks are between 70 and 79 grade is B
if marks are between 60 and 69 grade is C
if marks are less then 60 grade is D
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
char grade='A';
int marks;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Marks of student");
marks=sc.nextInt();
if((marks>=80) && (marks<=100))
{
grade='A';
}
else if ((marks>=70) && (marks<80))
{
grade='B';
}
else if ((marks>=60) && (marks<70))
{
grade='C';
}
else
{
grade='D';
}
System.out.println("Grade obtained by student is " + grade);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check whether marks are between 80 and 90
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int marks;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Marks of Student");
marks=sc.nextInt();
if((marks>=80) && (marks<=90))
{
System.out.println("Marks are between 80 and 90");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Marks are not between 80 and 90");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check whether alphabet is A or B using if statement
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
char alphabet;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Alphabet");
alphabet=sc.next().charAt(0);
if((alphabet=='A') || (alphabet=='B'))
{
System.out.println("Alphabet is either A or B");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Alphabet is neither A or B");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to check for vowel
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
char alphabet;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Alphabet");
alphabet=sc.next().charAt(0);
if((alphabet=='a') || (alphabet=='e') || (alphabet=='i') || (alphabet=='o') || (alphabet=='u'))
{
System.out.println("Alphabet is a vowel");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Alphabet is not a vowel");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Code to demonstrate for loop to print numbers from 1 to 10
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate while loop which prints numbers from 1 to 10
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i=1;
while(i<=10)
{
System.out.println("Value of i is " + i);
i++;
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java code to demonstrate do while loop
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i=1;
do
{
System.out.println("Value of i is " + i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}
Output
|
|
Another example of do while loop
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i=11;
do
{
System.out.println("Value of i is " + i);
i++;
}while(i<=10);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find factorial of number
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,i;
int fact=1;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number to find factorial for ");
a=sc.nextInt();
for(i=1;i<=a;i++)
{
fact=fact*i;
}
System.out.println("Factorial of number " + a + " is " + fact);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check whether number is prime or not
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,i;
boolean flag=true;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number to check for prime ");
a=sc.nextInt();
for(i=2;i<=a/2;i++)
{
if(a%i==0)
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(flag==true)
{
System.out.println("Number is Prime");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Number is not prime");
}
}
}
|
|
Java program to print fibonicci series
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a,b,c,i;
a=1;
b=1;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
a=b;
b=c;
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find sum of even numbers and odd numbers from a to b , a and b entered by user
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i,a,b,sumeven=0,sumodd=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter value for a ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value for b ");
b=sc.nextInt();
for(i=a;i<=b;i++)
{
if(i%2==0)
{
sumeven=sumeven+i;
}
else
{
sumodd=sumodd+i;
}
}
System.out.println("Sum of Even Numbers from " + a + " to " + b + " is " + sumeven);
System.out.println("Sum of Odd Numbers from " + a + " to " + b + " is " + sumodd);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check whether number is prime or not using while loop
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
boolean prime=true;
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter number to check for prime ");
a=sc.nextInt();
for(i=2;i<=a/2;i++)
{
if(a%i==2)
{
prime=false;
break;
}
}
if(prime==true)
{
System.out.println("Number is Prime ");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Number is not prime");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to print table of number
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i,a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Number to print table ");
a=sc.nextInt();
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
System.out.println(a + "x" + i + "=" + a*i);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find sum of digits of a number
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int num,digit;
int sum=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number to find sum of digits ");
num=sc.nextInt();
do
{
digit=num%10;
sum=sum+digit;
num=num/10;
}while(num!=0);
System.out.println("Sum of digits of number is " + sum);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to count number of digits in a number
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int num,digit;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number to find count of digits ");
num=sc.nextInt();
int count=0;
num=1234;
do
{
digit=num%10;
num=num/10;
count++;
}while(num!=0);
System.out.println("the number of digits in the number are " + count);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to check for reverse of a number
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int num,digit,rev=0;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number to find reverse of ");
num=sc.nextInt();
do
{
digit=num%10;
rev=(rev*10)+digit;
num=num/10;
}while(num!=0);
System.out.println("the reverse of number is " + rev);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate break statement in for loop
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(i=0;i<=10;i++)
{
if(i==5)
{
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program for continue statement
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(i=0;i<=10;i++)
{
if(i==5)
{
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Code to print integers using for loop with a gap of two numbers
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=10;i+=2)
{
System.out.println("Value of i is " + i);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to print pattern of stars and number of lines are taken by user
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n;
int i,j;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Number to print pattern of stars");
n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Pattern of Stars");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
System.out.print(j);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find factorial of number using decrement operator
import java.util.*;
class abc
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n;
int i,j;
int fact=1;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a number to find factorial using decrement operator");
n=sc.nextInt();
for(i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
fact=fact*i;
}
System.out.println("factorial of number is " + fact);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to create a function which displays hello world on the output screen
import java.util.*;
class phello
{
public void prhello()
{
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
phello ob=new phello();
ob.prhello();
}
}
Output
|
|
Increment / Decrement Operators
Java code to demonstrate Increment operator (++)
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a++;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying increment operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate decrement operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a--;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying decrement operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Short Hand Operators
Java program to demonstrate (+=) operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a+=2;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying (+=) operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate (-=) operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a-=2;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying (-=) operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to demonstrate (*=) operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a*=2;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying (*=) operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate (/=) operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a/=2;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying (/=) operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate (%=) operator
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Value of a is " + a);
a%=2;
System.out.println("Value of a after applying (%=) operator is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find largest numbers of three numbers using user defined function
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void findlargest(int a,int b,int c)
{
if((a>b) && (a>c))
{
System.out.println("Maximum Number of Three Numbers is " + a);
}
if((b>a) && (b>c))
{
System.out.println("Maximum Number of Three Numbers is " + b);
}
if((c>a) && (c>b))
{
System.out.println("Maximum Number of Three Numbers is " + c);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a,b,c;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter value for a ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value for b ");
b=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value for c ");
c=sc.nextInt();
findlargest(a,b,c);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to create a user defined function that finds smallest number of three numbers
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void findsmallest(int a,int b,int c)
{
if((a<b) && (a<c))
{
System.out.println("Smallest Number of Three Numbers is " + a);
}
if((b<a) && (b<c))
{
System.out.println("Smallest Number of Three Numbers is " + b);
}
if((c<a) && (c<b))
{
System.out.println("Smallest Number of Three Numbers is " + c);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a,b,c;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter value for a ");
a=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value for b ");
b=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter value for c ");
c=sc.nextInt();
findsmallest(a,b,c);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to create a function to check whether number is prime or not and number is passed as argument to the function and function returns a boolean value which is true for a prime number and false for not a prime number
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static boolean checkprime(int a)
{
boolean result=true;
int i;
for(i=2;i<=a/2;i++)
{
if(a%i==0)
{
result=false;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a;
boolean result=true;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a Number to check prime for ");
a=sc.nextInt();
result=checkprime(a);
if(result==true)
{
System.out.println("Number is prime ");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Number is not prime");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Program to create an array marks of size 5 and input the marks in 5 subjects and display the marks
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
final int size=5;
int marks[]=new int[size];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter marks of student in subject " + String.valueOf(i+1));
marks[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
for(int j=0;j<size;j++)
{
System.out.println("Marks of student in subject " + String.valueOf(j+1) + " " + marks[j]);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to create an array of marks of 5 subjects using while loop and display the marks
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
final int size=5;
int i=0,j=0;
int marks[]=new int[size];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(i<5)
{
System.out.println("Enter marks of student in subject " + String.valueOf(i+1));
marks[i]=sc.nextInt();
i++;
}
while(j<5)
{
System.out.println("Marks of student in subject " + String.valueOf(j+1) + " " + marks[j]);
j++;
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to create an array of a fix size as 5 and calculate total of 5 subject marks using for loop and display their average
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
final int size=5;
int i=0,j=0;
double total=0,average=0.0;
int marks[]=new int[size];
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
System.out.println("Enter value of marks in subject " + String.valueOf(i+1));
marks[i]=sc.nextInt();
total=total+marks[i];
}
average=total/size;
System.out.println("Total Marks are : " + total);
System.out.println("Average is : " + average);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Strings
Program to display charAt() function it displays character at a index
public class stringcharat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String a=new String("abcdef");
char ch;
ch=a.charAt(4);
System.out.println("character at index 4 is " + ch);
}
}
Output
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("abcdef");
char ch;
ch=a.charAt(4);
System.out.println("character at index 4 is " + ch);
}
}
Java program to compare two Strings using compareto functions
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("abc");
String b=new String("dfe");
int c;
c=b.compareTo(a);
System.out.println("value after comparing two strings is " + c );
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate concat function of String class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String ob=new String("abcdef");
String ob1=new String("abcxyz");
String ob2=new String();
ob2=ob.concat(ob1);
System.out.println("first string is " + ob);
System.out.println("second string is " + ob1);
System.out.println("concatenated string is " + ob2);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate contains method of String class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to check if it is part of String " + a);
b=sc.next();
if(a.contains(b)==true)
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " has String " + b);
}
else
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " does not contains String " + b);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to demonstrate endsWith String
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to check if it is end of the String " + a);
b=sc.next();
if(a.endsWith(b)==true)
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " has last alphabets as " + b);
}
else
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " does not have last alphabets as " + b);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate startsWith
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to check if it is beginning of the String " + a);
b=sc.next();
if(a.startsWith(b)==true)
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " has beginning alphabets as " + b);
}
else
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " does not have beginning alphabets as " + b);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Code to compare two strings for equality using equals method
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to check for equality with " + a);
b=sc.next();
if(a.equals(b)==true)
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " is equal to " + b);
}
else
{
System.out.println("String " + a + " is not equal to " + b);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate substring method
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
b=a.substring(0,3);
System.out.println("Part of String from index 0 to index 2 is "+b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java code to demonstrate equalsignorecase method
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a,b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter another String");
b=sc.next();
result=a.equalsIgnoreCase(b);
if(result==true)
{
System.out.println("Two Strings are equal if Upper Case and Lowercase is ignored ");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Two Strings are not equal if Upper Case and Lowercase is ignored ");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate index method of String class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
int c;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to find index of ");
b=sc.next();
c=a.indexOf(b);
if(c>=0)
{
System.out.println("Index of a in b is " + c);
}
else
{
System.out.println("Index of a in b is not valid index");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to find lastindexof method in a String
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
int c;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter a String to find last index of ");
b=sc.next();
c=a.lastIndexOf(b);
if(c>=0)
{
System.out.println("Last Index of a in b is " + c);
}
else
{
System.out.println("Last Index of a in b is not valid index");
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to demonstrate length method of String Class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
int c;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
c=a.length();
System.out.println("Length of String " + a + " is " + c);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to trim a String from both sides
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
a=a.trim();
System.out.println("String after applying trim function is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to convert a String to LowerCase
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
a=a.toLowerCase();
System.out.println("String converted to Lower Case is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
a=a.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("String converted to Upper Case is " + a);
}
}
Java Program to convert a String to Upper Case
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
a=a.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("String converted to Upper Case is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to reverse a String using StringBuilder Class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a;
String b;
boolean result=false;
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter a String");
a=sc.next();
StringBuilder c=new StringBuilder(a);
c=c.reverse();
System.out.println("Reversed String is " + c);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to demonstrate replace method
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String ob=new String("ABCDEFABC");
String ob1;
System.out.println("Original String is " + ob);
ob1=ob.replace('A', 'X');
System.out.println("String after replacement is " + ob1);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to demonstrate split method
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("abc def xyz ght bnhj");
String ab[]=a.split(" ");
int l,i;
l=ab.length;
for(i=0;i<l;i++)
{
System.out.println(ab[i]);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to demonstrate toCharArray method of String Class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("abcdef");
char arr[];
arr=a.toCharArray();
int i;
for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to Convert String to Int
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("12345");
int b;
b=Integer.parseInt(a);
System.out.println("Integer converted from string is " + b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Program to convert int variable to String Object
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a=1234;
String b;
b=String.valueOf(a);
System.out.println("String converted from int is " + b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java Program to convert float to String
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("123.45");
float b;
b=Float.parseFloat(a);
System.out.println("float converted from String is " + b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to convert float to String
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
float b=1234.5f;
String a;
a=String.valueOf(b);
System.out.println("String converted from float is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to convert String to double
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("123.45");
double b;
b=Double.parseDouble(a);
System.out.println("double converted from String is " + b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java program to convert double to String
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
double b=1234.5;
String a;
a=String.valueOf(b);
System.out.println("String converted from double is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Program to convert String to boolean
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
String a=new String("true");
boolean b;
b=Boolean.parseBoolean(a);
System.out.println("boolean converted from String is " + b);
}
}
Output
|
|
Program to convert boolean variable to String Class
import java.util.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String args[])
{
boolean b=true;
String a;
a=String.valueOf(b);
System.out.println("String converted from boolean is " + a);
}
}
Output
|
|
Java JDBC Connectivity
Program to connect to mysql table and display the records
import java.sql.*;
public class Javajdbc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Statement stmt;
ResultSet rs;
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/students";
Connection con =DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
stmt = con.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * from student");
System.out.println("Display all results:");
String str=new String();
int rno;
while(rs.next()){
rno=rs.getInt("rollno");
str = rs.getString("name");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(rno);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
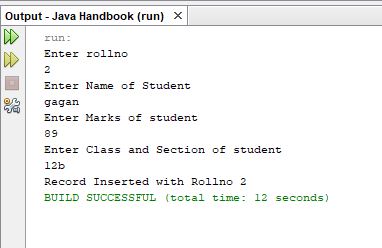
Program to connect to a mysql database and insert records in the table
import java.util.*;
import java.sql.*;
public class abc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO code application logic here
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int rollno;
System.out.println("Enter rollno");
rollno=sc.nextInt();
String name="";
System.out.println("Enter Name of Student ");
name=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter Marks of student ");
int marks;
marks=sc.nextInt();
String clas;
System.out.println("Enter Class and Section of student");
clas=sc.next();
try {
String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverName);
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/students";
Statement stmt;
int rs;
Connection con =DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
// Create a connection to the database
stmt = con.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeUpdate("insert into student values(" + rollno + ",'" + name + "'," + marks+",'" + clas + "')");
if(rs>0)
{
System.out.println("Record Inserted with Rollno " + rollno);
}
else
{
System.out.println("Record can't be inserted");
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
Output
Program to demonstrate jdbc prepared statement
import java.sql.*;
public class javajdbc2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String n="abcdef";
int rno=12;
int clas=11;
int marks=90;
String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverName);
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/students";
Statement stmt;
int rs;
Connection con =DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement("insert into student values(?,?,?,?)");
ps.setInt(1, rno);
ps.setString(2, n);
ps.setInt(3, clas);
ps.setInt(4, marks);
rs=ps.executeUpdate();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
|
|
Program to update a record in the table
import java.sql.*;
public class javajdbc2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverName);
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/students";
Statement stmt;
int rs;
Connection con =DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
stmt = con.createStatement();
int g;
g=stmt.executeUpdate("update student set name='abcghj' where rollno=1");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
|
|
program to insert image in mysql table
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.*;
class NewClass1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
FileInputStream fs=null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
String imagename="";
String imagepath="";
try
{
String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverName);
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/images";
//Step 1 : Connecting to server and database
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter Image Name");
imagename=sc.next();
System.out.println("Enter JPG File Path");
imagepath=sc.next();
File f=new File(imagepath);
fs=new FileInputStream(f);
ps= con.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO images VALUES(?,?)");
ps.setString(1, imagename);
ps.setBinaryStream(2,fs,(int)f.length());
ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("Image Stored Successfully");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.err.println("Cannot connect ! ");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
program to read image from mysql table
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.sql.*;
/**
*
* @author raman
*/
public class NewClass2 {
public static void main(String args[])
{
FileOutputStream fs=null;
try
{
String driverName = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
Class.forName(driverName);
String url ="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/images";
Statement stmt;
int rs;
Connection con =DriverManager.getConnection(url,"root", "");
//Step 1 : Connecting to server and database
PreparedStatement ps= con.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM images");
ResultSet rset=ps.executeQuery();
byte b[];
Blob blob;
int i=1;
while(rset.next())
{
File f=new File("c:\\temp\\abcde.jpg");
fs=new FileOutputStream(f);
blob=rset.getBlob("imagename");
b=blob.getBytes(1, (int)blob.length());
fs.write(b);
}
System.out.println("Image Read");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.err.println("Cannot connect ! ");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
program to read data from oracle database
import java.sql.*;
class NewClass3
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO code application logic here
try {
Statement stmt;
ResultSet rs;
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","waheguru345");
stmt = con.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * from students");
System.out.println("Display all results:");
String str=new String();
int rno;
int marks;
while(rs.next()){
rno=rs.getInt("rollno");
str = rs.getString("name");
marks=rs.getInt("marks");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(rno);
System.out.println(marks);
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
|
|
program to read image from oracle database
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.sql.*;
/**
*
* @author raman
*/
public class NewClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO code application logic here
try {
Statement stmt;
int rs;
FileOutputStream fs=null;
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe","system","waheguru345");
PreparedStatement ps= con.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM images");
ResultSet rset=ps.executeQuery();
byte b[];
Blob blob;
int i=1;
while(rset.next())
{
File f=new File("c:\\temp\\abcdefromoracle.jpg");
fs=new FileOutputStream(f);
blob=rset.getBlob("image");
b=blob.getBytes(1, (int)blob.length());
fs.write(b);
}
System.out.println("Image Read");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class student that contains two public member functions getdata() and showdata() and four data members (rollno,name,clas and marks)
class student
{
private int rollno;
private String name;
private int marks;
private int clas;
public void getdata()
{
rollno=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
marks=80;
clas=11;
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno of the student is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name of student is " + name);
System.out.println("marks of student are " + marks);
System.out.println("class of student is " + clas);
}
}
public class classstudent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student ob=new student();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class employee that contains two public member functions getdata() and showdata() and four data members (ecode,name,salary and designation)
class employee
{
private int ecode;
private String name;
private float salary;
private String designation;
public void getdata()
{
ecode=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
salary=10000;
designation=new String("Employee");
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("employee code is " + ecode);
System.out.println("name of employee is " + name);
System.out.println("salary of employee is " + salary);
System.out.println("designation of employee is " + designation);
}
};
public class classemployee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
employee ob=new employee();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class book that contains two public member functions getdata() and showdata() and four data members (bookid,name,price and author)
class book
{
private int bookid;
private String name;
private float price;
private String author;
public void getdata()
{
bookid=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
price=300;
author=new String("abcxyz");
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("book id is " + bookid);
System.out.println("book name is " + name);
System.out.println("price of book is " + price);
System.out.println("author of the book is " + author);
}
};
public class classbook {
public static void main(String[] args) {
book ob=new book();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to create a class box with data members (width,depth and height) and member functions (getdata,showdata and volume)(volume member function calculates the volume of the box )
class box
{
private int width;
private int depth;
private int height;
public void getdata()
{
width=10;
depth=20;
height=30;
}
public void volume()
{
int vol;
vol=width*depth*height;
System.out.println("volume of box is " + vol);
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("width of box is "+ width);
System.out.println("depth of box is " + depth);
System.out.println("height of box is " + height);
}
};
public class classbox {
public static void main(String[] args) {
box ob=new box();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
ob.volume();
}
}
program to create a class box with data members (width,depth and height) and member functions (getdata,showdata and volume)(volume member function calculates the volume of the box )
class box
{
private int width;
private int depth;
private int height;
public void getdata()
{
width=10;
depth=20;
height=30;
}
public void volume()
{
int vol;
vol=width*depth*height;
System.out.println("volume of box is " + vol);
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("width of box is "+ width);
System.out.println("depth of box is " + depth);
System.out.println("height of box is " + height);
}
};
public class classbox {
public static void main(String[] args) {
box ob=new box();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
ob.volume();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class employee with data members as ecode,ename,designation,basic,hra,da and total) calculate total function calculates the total salary as sum of basic,da and hra , getdata function inputs data from user and showdata member function displays data
class employeesal
{
private int ecode;
private String ename;
private float basic;
private float da;
private float hra;
private float total;
private String designation;
public void getdata()
{
ecode=1;
ename=new String("abcdef");
designation=new String("employee");
basic=10000;
da=3000;
hra=2000;
}
public void calculatetotal()
{
total=basic+da+hra;
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("employee code is " + ecode);
System.out.println("employee name is " + ename);
System.out.println("employee designation is " + designation);
System.out.println("total salary (basic+da+hra) is " + total);
}
}
public class classsalary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
employeesal ob=new employeesal();
ob.getdata();
ob.calculatetotal();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate a class studentone which has a parameterized method
class studentone
{
private int rollno;
private String name;
private int marks;
private int clas;
public void getdata(int rno,String n,int m,int cl)
{
rollno=rno;
name=n;
marks=m;
clas=cl;
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno of the student is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name of student is " + name);
System.out.println("marks of student are " + marks);
System.out.println("class of student is " + clas);
}
}
public class classstudentparameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentone ob=new studentone();
ob.getdata(1,"abcdef",80,11);
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate a class boxone which has a method that returns a value
class boxone
{
private int width;
private int depth;
private int height;
public void getdata()
{
width=10;
depth=20;
height=30;
}
public int volume()
{
int vol;
vol=width*depth*height;
return vol;
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("width of box is "+ width);
System.out.println("depth of box is " + depth);
System.out.println("height of box is " + height);
}
};
public class classboxreturn {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int v;
boxone ob=new boxone();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
v= ob.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of box is " + v);
}
}
program to demonstrate nested classes
class marks
{
private int physics;
private int maths;
private int chemistry;
public void getmarks(int p,int m,int c)
{
physics=p;
maths=m;
chemistry=c;
}
public void showmarks()
{
System.out.println("marks in physics are " + physics);
System.out.println("marks in maths are " + maths);
System.out.println("marks in chemistry are " + chemistry);
}
}
class studentmarks
{
private int rollno;
private String name;
private int clas;
private marks ma;
public void getdata()
{
rollno=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
clas=11;
ma=new marks();
ma.getmarks(89,90,91);
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno of student is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name of student is "+ name);
System.out.println("class of student is " + clas);
ma.showmarks();
}
}
public class nestedclass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentmarks ob=new studentmarks();
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate static data members and methods
class studentst
{
int rollno;
String name;
int marks;
int clas;
static int count;
studentst()
{
count++;
}
public void getdata()
{
rollno=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
marks=90;
clas=11;
}
public void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno of the student is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name of student is " + name);
System.out.println("marks of student are " + marks);
System.out.println("class of student is " + clas);
}
public static void showcount()
{
System.out.println("number of objects created are " + count);
}
};
public class staticcount {
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentst ob=new studentst(); //object of class student created
ob.getdata();
ob.showdata();
studentst ob1=new studentst();
studentst ob2=new studentst();
studentst ob3=new studentst();
studentst.showcount();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class student with data members (rollno, name, marks, clas) and contains member functions (showdata), class also contains a default constructor which initializes the data members
class student
{
int rollno;
String name;
int marks;
int clas;
public student() //a default constructor
{
rollno=10;
name=new String("abcdef");
marks=90;
clas=11;
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno of student is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name of student is " + name);
System.out.println("marks of student are " + marks);
System.out.println("class of student is " + clas);
}
}
public class studentcons {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student ob=new student(); //object of class student is created and constructor is called which initialises the data members
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class employee with data members (ecode,ename,salary and designation) and contains member functions (showdata), class also contains a default constructor which initializes the data members
class employee
{
int ecode;
String ename;
int salary;
String designation;
public employee()
{
ecode=1;
ename=new String("abcdef");
salary=10000;
designation=new String("xyzxyz");
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("employee code is " + ecode);
System.out.println("employee name is " + ename);
System.out.println("employee salary is " + salary);
System.out.println("employee designation is " + designation);
}
}
public class employeecons {
public static void main(String[] args) {
employee ob=new employee();
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate example of class bankaccount with data members ( account_no,name,type,balance) and contains member functions (deposit,withdraw and showdata), class also contains a default constructor
class account
{
int account_no;
String name;
char type;
int balance;
public account()
{
account_no=1001;
name=new String("abcdef");
type='s';
balance=1000;
}
void deposit(int amount)
{
balance=balance+amount;
System.out.println(amount + " deposited in account no " + account_no);
}
void withdraw(int amount)
{
if(balance>=1000)
{
balance=balance=amount;
System.out.println(amount + " withdrawn from account no " + account_no);
}
else
{
System.out.println("amount can't be withdrawn (balance in account is less than 1000 ");
}
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("account no is " + account_no);
System.out.println("name of account is " + name);
if(type=='s')
{
System.out.println("type of account is savings");
}
else
{
System.out.println("type of account is current");
}
System.out.println("balance in the account is " + balance);
}
}
public class bankaccountcons {
public static void main(String[] args) {
account ob=new account();
ob.showdata();
ob.deposit(3000);
ob.withdraw(2000);
ob.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate parameterized constructor in class student
class studentone
{
int rollno;
String name;
int marks;
int clas;
public studentone(int srollno,String sname,int smarks,int sclas)
{
rollno=srollno;
name=sname;
marks=smarks;
clas=sclas;
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name is " + name);
System.out.println("marks are " + marks);
System.out.println("class is " + clas);
}
};
public class studentconsparameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
studentone ob=new studentone(1,"abcdef",90,12);
ob.showdata();
studentone ob1=new studentone(2,"abcxyz",88,11);
ob1.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate parameterized constructor in class employee
class employeeone
{
int ecode;
String ename;
int esalary;
String edesignation;
public employeeone(int code,String name,int salary,String designation)
{
ecode=code;
ename=name;
esalary=salary;
edesignation=designation;
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("employee code is "+ ecode);
System.out.println("employee name is " + ename);
System.out.println("employee salary is " + esalary);
System.out.println("employee designation is " + edesignation);
}
};
public class employeeconsparameter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
employeeone ob=new employeeone(1,"abcdef",10000,"xyxyx");
ob.showdata();
employeeone ob1=new employeeone(2,"abcxyz",20000,"abcabc");
ob1.showdata();
}
}
program to demonstrate constructor overloading in class student
class studenttwo
{
int rollno;
String name;
int marks;
int clas;
public studenttwo() //constructor 1
{
rollno=1;
name=new String("abcdef");
marks=90;
clas=11;
}
public studenttwo(int srollno) //constructor 2
{
rollno=srollno;
name=new String("abcdef");
marks=90;
clas=11;
}
public studenttwo(int srollno,String sname) //constructor 3
{
rollno=srollno;
name=sname;
marks=90;
clas=11;
}
public studenttwo(int srollno,String sname,int smarks) //constructor 4
{
rollno=srollno;
name=sname;
marks=smarks;
clas=11;
}
public studenttwo(int srollno,String sname,int smarks,int sclas) //constructor 5
{
rollno=srollno;
name=sname;
marks=smarks;
clas=sclas;
}
void showdata()
{
System.out.println("rollno is " + rollno);
System.out.println("name is " + name);
System.out.println("marks are " + marks);
System.out.println("class is " + clas);
}
};
public class consoverloading {
public static void main(String[] args) {
studenttwo ob1=new studenttwo(); //constructor 1 called here
ob1.showdata();
studenttwo ob2=new studenttwo(2); //constructor 2 called here
ob2.showdata();
studenttwo ob3=new studenttwo(3,"derdre"); // constructor 3 called here
ob3.showdata();
studenttwo ob4=new studenttwo(4,"abcdef",89); // constructor 4 called here
ob4.showdata();
studenttwo ob5=new studenttwo(5,"xyxyz",90,11); //constructor 5 called here
ob5.showdata();
}
}
program to inherit a class boxweight from class from box
class box
{
double width;
double height;
double depth;
box(box ob)
{
width=ob.width;
height=ob.height;
depth=ob.depth;
}
box(double w,double h,double d)
{
width=w;
height=h;
depth=d;
}
box()
{
width=-1;
height=-1;
depth=-1;
}
box(double len)
{
width=height=depth=len;
}
double volume()
{
return width*height*depth;
}
}
class boxweight extends box
{
double weight;
boxweight(double w,double h,double d,double m)
{
width=w;
height=h;
depth=d;
weight=m;
}
}
public class boxinheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boxweight box1=new boxweight(10,20,15,34.3);
boxweight box2=new boxweight(2,3,4,0.076);
double vol;
vol=box1.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of box1 is " + vol);
System.out.println("Weight of box1 is " + box1.weight);
vol=box2.volume();
System.out.println("Volume of box2 is " + vol);
System.out.println("Weight of box2 is " + box2.weight);
}
}
program to demonstrate exception class
public class exception {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int a=args.length;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
int b=42/a;
int c[]={1};
c[42]=99;
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception : " + e);
}
}
}
program to demonstrate exception arithmetic exception
public class arithmeticexception {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int d,a;
try{
d=0;
a=42/d;
System.out.println("this will not be printed");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Division By Zero");
}
System.out.println("After catch statement");
}
}
program to display description of exception
public class exceptiondescription {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int d,a;
try{
d=0;
a=42/d;
System.out.println("this will not be printed");
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Exception : " + e);
}
System.out.println("After catch statement");
}
}
program to demonstrate finally keyword
package javaexceptions;
public class exceptionfinally {
static void proca()
{
try{
System.out.println("inside proca");
throw new RuntimeException("demo");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("proca finally");
}
}
static void procb()
{
try{
System.out.println("inside procb");
return;
}
finally
{
System.out.println("procb finally");
}
}
static void procc()
{
try
{
System.out.println("inside procc");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("procc finally");
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
try{
proca();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception caught");
}
procb();
procc();
}
}
program to create subclass of exception class
class MyException extends Exception
{
private int detail;
MyException(int a)
{
detail=a;
}
public String toString()
{
return "MyException[" + detail + "]";
}
}
public class exceptionsublass {
static void compute(int a) throws MyException
{
System.out.println("Called compute(" + a + ")");
if(a>10)
throw new MyException(a);
System.out.println("Normal exit");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
try{
compute(1);
compute(20);
}
catch(MyException e)
{
System.out.println("Caught " + e);
}
}
}
program to demonstrate throws keyword
public class throwsexception {
static void throwone() throws IllegalAccessException{
System.out.println("inside throwone");
throw new IllegalAccessException("demo");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
throwone();
}
catch(IllegalAccessException e)
{
System.out.println("Caught " + e);
}
}
}
program to demonstrate multiple catch clauses
public class multiplecatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int a=args.length;
System.out.println("a = " + a);
int b=42/a;
int c[]={1};
c[42]=99;
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("Divide by 0 : " + e);
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("Array index out of bounds " + e);
}
}
}
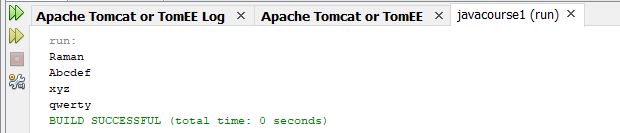
package javacourse1;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.*;
public class NewClass5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File myObj = new File("c:\\temp\\barchart.txt");
Scanner myReader = new Scanner(myObj);
while (myReader.hasNextLine()) {
String data = myReader.nextLine();
System.out.println(data);
}
myReader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
Write Data to File
import java.io.File; // Import the File class
import java.io.IOException; // Import the IOException class to handle errors
public class NewClass6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File myObj = new File("c:\\temp\\barchart1.txt");
if (myObj.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("File created: " + myObj.getName());
} else {
System.out.println("File already exists.");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
Write Data to File
import java.io.FileWriter; // Import the FileWriter class
import java.io.IOException; // Import the IOException class to handle errors
public class NewClass7{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileWriter myWriter = new FileWriter("c:\\temp\\abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz.txt");
myWriter.write("Data");
myWriter.close();
System.out.println("Successfully wrote to the file.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
Append Data to File
import java.io.FileWriter; // Import the FileWriter class
import java.io.IOException; // Import the IOException class to handle errors
public class WriteToFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileWriter myWriter = new FileWriter("filename.txt",true);
myWriter.write("Files in Java might be tricky, but it is fun enough!");
myWriter.close();
System.out.println("Successfully wrote to the file.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Write Data to File
import java.io.FileWriter; // Import the FileWriter class
import java.io.IOException; // Import the IOException class to handle errors
public class WriteToFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileWriter myWriter = new FileWriter("filename.txt",true);
myWriter.write("Files in Java might be tricky, but it is fun enough!");
myWriter.close();
System.out.println("Successfully wrote to the file.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// Java Program to create a Client
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass8 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String serverName = "localhost";
int port = 2334;
try {
System.out.println("Connecting to " + serverName + " on port " + port);
Socket client = new Socket(serverName, port);
System.out.println("Just connected to " + client.getRemoteSocketAddress());
OutputStream outToServer = client.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(outToServer);
out.writeUTF("Hello from " + client.getLocalSocketAddress());
InputStream inFromServer = client.getInputStream();
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(inFromServer);
System.out.println("Server says " + in.readUTF());
client.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
|
// Java Program to create a ServerSocket
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class NewClass9 extends Thread {
private ServerSocket serverSocket;
public NewClass9(int port) throws IOException {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
serverSocket.setSoTimeout(10000);
}
public void run() {
while(true) {
try {
System.out.println("Waiting for client on port " +
serverSocket.getLocalPort() + "...");
Socket server = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("Just connected to " + server.getRemoteSocketAddress());
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(server.getInputStream());
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(server.getOutputStream());
out.writeUTF("Thank you for connecting to " + server.getLocalSocketAddress()
+ "\nGoodbye!");
server.close();
} catch (SocketTimeoutException s) {
System.out.println("Socket timed out!");
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String [] args) {
int port = 2345;
try {
Thread t = new NewClass9(port);
t.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// Java program to demonstrate BufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Enter data using BufferReader
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// Reading data using readLine
String name = reader.readLine();
// Printing the read line
System.out.println(name);
}
}
|
|
Program to take user input using Scanner Class
import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
*
* @author raman
*/
public class NewClass10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object
System.out.println("Enter username");
String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input
System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input
}
}
|
|
// Java program to demonstrate abs function
import java.lang.Math;
public class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// get some doubles to find their absolute values
double x = 4876.1874d;
double y = -0.0d;
// get and print their absolute values
System.out.println("Math.abs(" + x + ")=" + Math.abs(x));
System.out.println("Math.abs(" + y + ")=" + Math.abs(y));
System.out.println("Math.abs(-9999.555d)=" + Math.abs(-9999.555d));
}
}
// Java program to read image in jlabel
String imagename;
ImageIcon ic=new ImageIcon(imagename);
jLabel4.setIcon(ic);
Program to take user input using Scanner Class
import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object
System.out.println("Enter username");
String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input
System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input
}
}
Java program to create an ArrayList and run Iterator to get Values
import java.util.*;
public class NewClass {
public static void main(String args[])
{
ArrayList arr=new ArrayList();
arr.add("Raman");
arr.add("Abcdef");
arr.add("xyz");
arr.add("qwerty");
Iterator itr=arr.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}